NLP in 2025: From Classification to Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Natural language processing (NLP) has matured from mere text classification tasks to systems having the capabilities of searching, reasoning, and generating high-quality content that is even backed by your own data. One of the most significant trends in 2025 is retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) which merges search and large language models to create applications that are not only more accurate but also more reliable.
Traditional NLP was limited to performing simple activities such as sentiment analysis, topic modeling, and intent classification using bag-of-words, TF–IDF, and standard ML models. Such systems might have been good at performing very specific tasks, but they also demanded a lot of feature engineering and had problems processing nuances and long contexts.
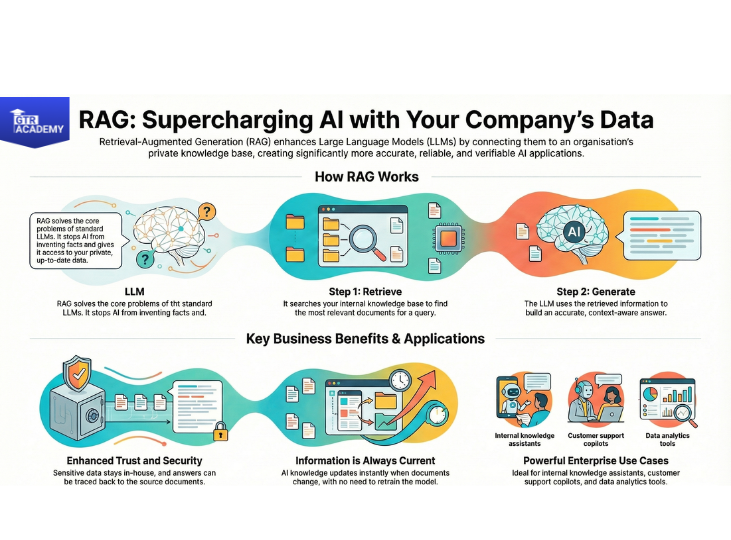
Through learning deep representations from vast text corpora, large language models (LLMs) have become capable of performing various (summarization, Q&A, translation, classification) with very little task-specific training. Still, “pure” LLMs carry two major problems: they can invent and do not have access to your private or latest data.
RAG resolves these problems by employing the following two parts:
- Retrieval: A step in the search process that obtains the most suitable documents, fragments, or records out of your knowledge base (let’s say PDFs, wiki pages, tickets, product docs) given a query.
- Generation: An LLM which goes through the retrieved snatches of text and then forms the answer based on them.T he model is not answering only on the basis of its training data but rather, it is answering ”based upon” the retrieved context, which is under your control and you can keep it updated. Consequently, hallucinations are considerably lowered and answers get more verifiable.